Medhyterra, a low-carbon ammonia import terminal on the Fos Tonkin site
The Medhyterra project involves redeveloping part of the site of Elengy's Fos Tonkin LNG terminal into a low-carbon ammonia import terminal. This first step in the implementation of Elengy's strategy would contribute to supplying the Fos region with low-carbon molecules, either directly in the form of ammonia, or in the form of hydrogen after possible cracking downstream of the terminal.
About the project
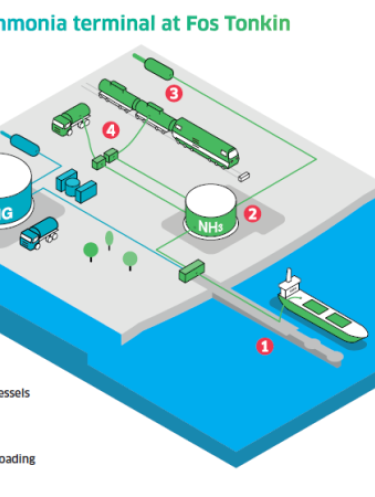
The Medhyterra project aims to redevelop part of the Fos Tonkin terminal into a low-carbon ammonia import, storage and distribution terminal.
It would include ;
- reception and transfer facilities to accommodate ships carrying low-carbon ammonia, which would then be stored in a tank with a capacity of around 30,000 m3
- loading bays for wagons, to transport the ammonia by rail, and for tankers, as well as a pipeline to distribute the ammonia out of the terminal.
- Ultimately, the terminal should receive more than 200,000 tonnes of low-carbon ammonia per year.
A historic industrial base open to the Mediterranean
The project to redevelop part of the Fos Tonkin terminal into a low-carbon ammonia import terminal is of strategic importance in the current context of energy transition and decarbonisation of industry.
The redevelopment of the terminal would make it possible to capitalise on the existing infrastructure while incorporating new facilities for receiving and storing ammonia. As an energy carrier, low-carbon ammonia offers advantages for the transport and storage of low-carbon hydrogen, which is essential for reducing carbon emissions.
These developments support the objectives of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the 2050 target set by the European Union for achieving carbon neutrality, by promoting the use of cleaner, more sustainable energy.
Key figures
- Storage tank capacity of around 30,000 m3
- Import capacity of 200,000 tonnes of low-carbon ammonia per year
- 10 to 15 ships unloaded per year
- Estimated investment of between €120 million and €150 million
- Final investment decision expected in 2026
- Commissioning scheduled for 2029
About low-carbon ammonia
Ammonia is synthesised from nitrogen, a neutral gas naturally present in the air, and hydrogen. In its low-carbon version, it can :
- contribute to decarbonising industries that use it directly in their processes (agriculture, petrochemicals, automotive)
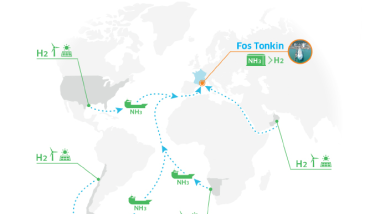
- provide a solution for transporting low-carbon hydrogen produced in regions of the world with significant renewable electricity resources to regions where the need for low-carbon hydrogen will not be met by local production.
Prior consultation
From 14 October to 24 November 2024, Elengy engaged in dialogue with the residents and stakeholders of Fos-sur-Mer during a voluntary preliminary consultation on the Medhyterra project. The last public meeting, a summary meeting of the Medhyterra project consultation, was held on Monday 18 November in Fos-sur-Mer in front of a large audience.
Corinne Larrue and Ginette Vastel, who acted as guarantors for the Commission nationale du débat public (CNDP) during this preliminary consultation, now have until 24 December 2024 to draw up a report on this process of dialogue with the region. Elengy will then have two months to respond to the recommendations of the guarantors.
All these documents will be made public and posted online on the consultation website.
