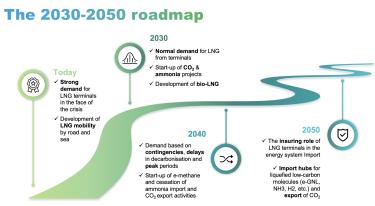
Our strategy


The energy sector is going through a period of upheaval that requires all its players, including Elengy, to reinvent themselves. That's why we launched our ‘Reinventing 2025’ corporate project in 2021. This was the start of a profound change, which we have translated into a strong ambition: ‘Successfully diversify into new gases and services to accelerate towards a carbon-neutral world.’
In 2023, this ambition is reflected in our new strategic priorities, which are resolutely focused on decarbonisation.
Our 3 development priorities
Our LNG terminals, located at the crossroads of energy chains, will play a key role as import points for low-carbon molecules and export gateways for CO2 destined for permanent storage. Elengy will also play an active role in the development of liquefied biomethane (bioGNL) and low-carbon hydrogen.
From now on, Elengy is taking a decarbonising approach based on 3 main strategic priorities.
Decarbonising our assets and activities
with the maintenance of our sites in operational condition, the improvement of our environmental impact and the accelerated switch to green LNG.
Decarbonising heavy mobility on land and sea
in which terminals and LNG play a central role.
Decarbonizing industries
with imports of new low-carbon molecules (hydrogen, ammonia, etc.) and solutions for liquefying and exporting industrial CO2.
New molecules in our terminals
Elengy is developing projects aimed at adapting its terminals to turn them into CO2 liquefaction and export sites, and developing them into decarbonisation hubs using ammonia. Elengy is actively promoting the introduction of e-methane production, which has the advantage of not requiring any adaptation of existing logistics chains or customer installations.
In addition, a new tax incentive introduced by the 2024 Finance Law (TIRUERT) will make it possible to market bioNGL at a price competitive with diesel, with no link to the market price of gas. Drawing on our expertise in cryogenics and working with innovative partners, we are developing ‘on-farm’ liquefaction projects that are true models of the circular economy.
In this way, Elengy's terminals will become major infrastructures in the energy transition.
CO2
CO2 is a colourless, odourless gas present in the atmosphere at 400 ppm (a figure that has been rising over the years). Unlike natural gas, it has to be compressed beyond 5 bars to become liquid. It is a major greenhouse gas. It is also a waste product subject to a European tax known as ‘CO2 quotas’.
Ammonia
is a chemical compound with the formula NH3, which is gaseous under normal conditions of temperature and pressure. Liquid at -33°C, it can be easily transported, stored and moved by road, rail or pipeline. Tomorrow, it will be synthesised from green hydrogen and will be used to transport green hydrogen from one continent to another, and could be the fuel of the future to decarbonise the maritime sector.
E-methane
is a synthetic gas produced from renewable hydrogen and recycled CO2. It is used to convert non-storable electricity into a storable renewable gas and recovers the CO2 released by industrial sites or extracted from biogas during the purification phase. It can be stored and injected directly into the grid, without prior adaptation of consumer infrastructures and installations. Thanks to e-methane, the CO2 released is given a new life, helping to reduce the overall carbon footprint.
Le bio-LNG
is the renewable, non-fossil fuel variant of LNG, produced from organic matter such as waste and residues. The organic matter is transformed into biogas in a fermenter. This biogas is then purified and liquefied to produce a gas with the same properties as liquefied natural gas. With a carbon footprint more than 80% lower than that of diesel, it contributes to the objectives of decarbonising the heavy land and sea mobility sector, and to the consumption/production targets for renewable gas set by the French Energy Transition law.
Nos projets en développement
Aujourd’hui, Elengy a l’ambition de transformer ses terminaux méthaniers en hub multiservices de décarbonation, notamment pour les chaînes de capture et de stockage du carbone (CCS) ainsi que pour de nouvelles molécules : bio-GNL, hydrogène et ammoniac bas carbone.

Successful GOCO2 Calls For Expressions of Interest to decarbonise industry in the Greater-Western area in France.
18 July 2024
As part of their commitment to the energy transition, GRTgaz, France's main gas transmission operator, and Elengy, the incumbent operator of LNG terminals in France[...]

Elengy announces the launch of preliminary consultations regarding a low-carbon ammonia import terminal project at its Fos Tonkin site
08 July 2024
Elengy, an expert in liquefied natural gas (LNG) and a pioneering operator of LNG terminals in France, has voluntarily engaged with the National Commission for Public[...]
Rhône CO2: SPSE and Elengy join forces to accelerate the development of CO2 transport, liquefaction and export infrastructures for industrial companies in the Rhône Valley and the Fos-sur-Mer industrial port area.
03 June 2024
Fabien Poure, CEO of SPSE, and Nelly Nicoli, CEO of Elengy, announce the joint launch of a Call for Expressions of Interest (AMI "Rhône CO2") to develop a network[...]
